
Featured Photo by Quartl / CC BY-SA 3.0
A field guide on how to identify and propagate Guelder Rose (Viburnum opulus), a deciduous shrub that is native to Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia.
It has been introduced into North America and is present near the great lakes and Acadian forests.
How to Identify Guelder Rose (Viburnum opulus)
Leaves

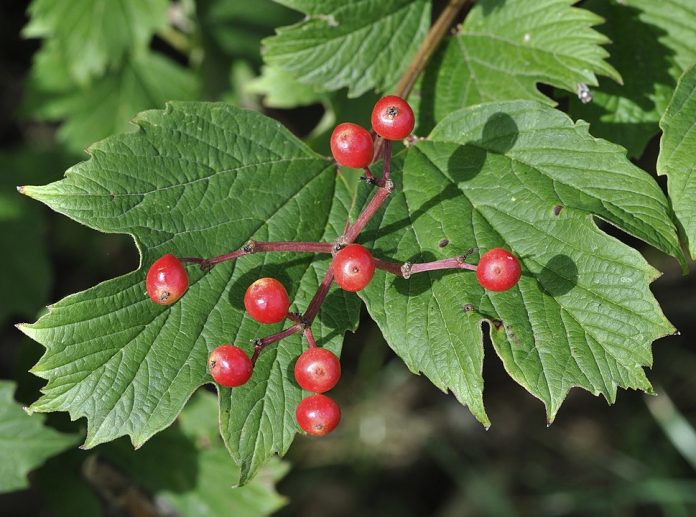
Guelder Rose Viburnum leaves are elliptical-shaped with lobate margins (3-5 lobes) and have a serrated margin. The leaves grow on the stems in opposite arrangements.
Fruit
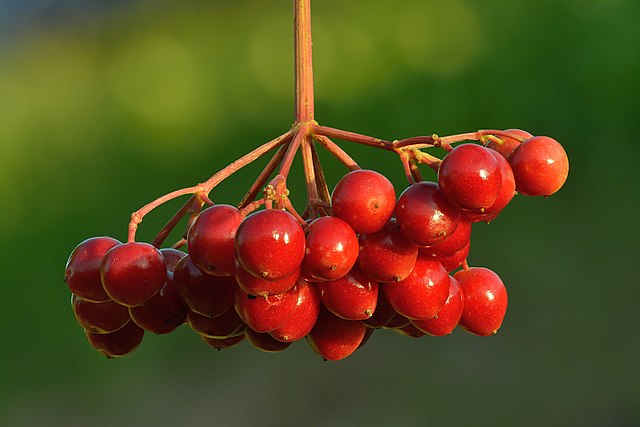

The fruit of Guelder Rose Viburnum is a bright red or translucent berry-like drupe that is 7-10 mm in diameter. It contains a single seed and persists on the shrub through winter.
Flower

The flowers of Guelder Rose Viburnum are white, flat-topped clusters with a diameter of 5-15 cm. Each individual flower has five petals and is 3-5 mm in diameter.
Flowering Season
Guelder Rose Viburnum typically blooms from May to June.
Habitat
Guelder Rose Viburnum prefers moist soils and can be found growing in woodlands, hedgerows, and on riverbanks.
Some other understory plants that associate with guelder rose are:
- Wild Rose (Rosa acicularis)
- Redosier Dogwood (Cornus sericea)
- Beaked Hazelnut (Corylus cornuta)
Wildlife Value
The fruit of Guelder Rose Viburnum is an important food source for many bird species, including thrushes, blackbirds, and waxwings. The shrub also provides shelter and nesting habitat for birds.
How to Propagate Guelder Rose (Viburnum opulus)

Hardiness Zone: 3-8
Soil Type: Well-drained clay, loam, sand.
Water: Moist.

Exposure: Full Sun to Partial Shade.
You can propagate guelder rose with two effective methods:
- Stem Cuttings: The best time to take stem cuttings is in early summer when the shrub is actively growing. Cuttings should be 10-15 cm long and taken from the current year’s growth.
- By Seed: Guelder rose seeds require 90-day warm, 60-day cold stratification before they will germinate. This means it can take quite some time to prepare the seeds and see any growth. Nevertheless, it’s still an effective propagation method for large-scale growing.
How to Propagate Guelder Rose (Viburnum opulus) by Seed
If you can identify wild Guelder Rose Viburnum, then you can harvest their seeds easily.
How to Harvest Seeds
Harvesting: Wait until the fruit is fully ripe, then remove the pulp and extract the seeds. Usually, that is late summer to early fall.
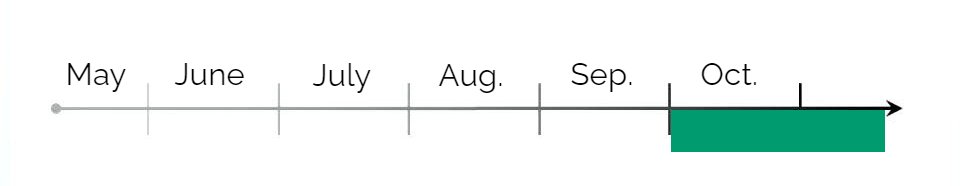
Stratification: Seeds need to undergo a period of warm-cold stratification to break their dormancy. Store the seeds in moist sand or peat moss at room temperature for 90 days, then in the refrigerator for 60 days.
Sowing: Sow the seeds in a seed tray or individual pots in early spring, at 3/8″ depth. Cover lightly with soil and water.
Germination: Viburnum seeds are slow to germinate and can take several months. Keep the soil moist and place the tray or pots in a warm, bright location.
How to Propagate Guelder Rose (Viburnum opulus) by Cuttings
If you’re looking to propagate guelder rose, the best method is from cuttings. Here are some tips on how to do it:
Timing: The best time to take cuttings is during the semi-hardwood stage, which is when the current year’s growth is starting to harden. Wait at least 6 weeks after the first leaves of spring to ensure that the stems are mature enough for cutting.

Cutting Length: Aim for 4-5 inches for each cutting, with 2 pairs of nodes. Make sure to use clean, sharp pruning shears to prevent damage to the stems.
Rooting Soil: Use a well-draining rooting medium, such as coarse sand or perlite, to propagate guelder rose cuttings. Make sure the soil is moist but not waterlogged.
Duration: Allow the cuttings to root throughout the summer without disturbing them. Keep them in a warm, bright location but out of direct sunlight.
Wintering: Bring the cuttings indoors to overwinter, or cover them with a layer of mulch or snow if they are in an outdoor location.
Transplant Time: In the spring, re-pot the cuttings in a good compost/soil mix once they start to show signs of new growth. Make sure to add some slow-release fertilizing granules to promote healthy growth.
Sunlight and Watering: Place the rooted cuttings in a sunny location and water regularly to ensure proper growth.
Guelder rose is a species of viburnum, and they all propagate in a similar way. If you want to learn more about propagating viburnum, take a look at our parent article:

FAQ
A: Yes, Guelder Rose can be toxic if ingested in large quantities. The plant contains a variety of toxins, including viburnin and tannins, which can cause gastrointestinal upset, vomiting, and diarrhea in pets and humans.
A: While Guelder Rose can tolerate some sun, it prefers partial shade or dappled sunlight. Too much direct sunlight can cause leaf scorching and dehydration.
A: The best time to prune Guelder Rose is in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. Pruning can help maintain the shape of the plant and encourage healthy growth.
A: Guelder Rose prefers consistently moist soil, but overwatering can lead to root rot. Water the plant deeply once a week, and adjust the frequency based on weather conditions and soil moisture.
A: Guelder Rose is susceptible to a variety of pests and diseases, including aphids, spider mites, powdery mildew, and leaf spot. Regularly inspecting the plant and treating any infestations or diseases promptly can help keep it healthy. Check out some eco-friendly pest control methods.
