A field guide on how to identify and propagate Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain (Goodyera repens), an evergreen zone 2 perennial shrub that is native to North America.
Dwarf rattlesnake plantain is a rare plant in North America, as a matter of fact, I’ve wandered the boreal forest for 4 years as a tree planter before I saw it.
It seems to be very particular about where it likes to grow, and further research on it confirmed this.
Dwarf rattlesnake plantain is actually a late succession plant, which means it will grow in aged forests in its late successional cycle.
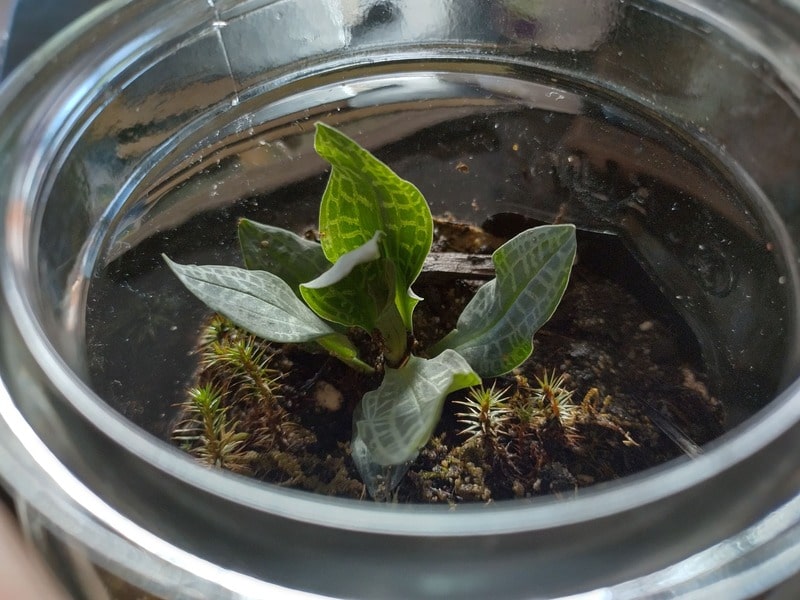
When I found some myself, I took a few specimens back with me and collected some of their seeds.
At that point, I hadn’t known it was a rare plant, but knowing that, I’m glad I did since I now have samples at home with me and can experiment with its propagation.
In this guide, you can expect to see some information on the identification of dwarf rattlesnake plantain, as well as some of my notes regarding its propagation:
Table of Content:
Let’s get right to it!
How to Identify Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain (Goodyera repens)
Leaves
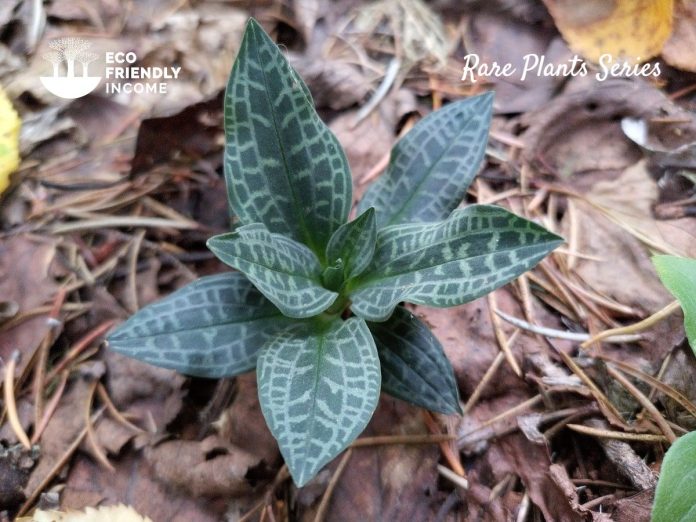
To identify dwarf rattlesnake plantain, look for basal leaves that are dark green and have a leathery texture. The leaves should also be arranged in a rosette pattern.
The leaf is lanceolate to oblong-lanceolate in shape, with entire margins, and has a silvery-white stripe design.
Flowers

The flowers of the dwarf rattlesnake plantain (Goodyera repens) are small, white, and borne in loose clusters on a stalk that arises from the leaf axils.
The flower stalk and sepals are covered in tiny hairs.
Their flowers are amongst the tiniest of flowers found in the orchid family.
Flowering Season
Dwarf rattlesnake plantain flowers bloom from mid-summer to early fall.
Habitat
You can find Goodyera repens in woodlands, bogs, and damp, shady areas.
Look for it in conifer or mixed tree stands at least 70 years old.
I found my specimens in a sandy conifer forest undergrowth through moss and leaf litter.
Wildlife Value
Dwarf rattlesnake plantain, being an orchid, is an important plant for many boreal forest insect pollinators such as bumblebees.
Mycoheterotrophy

Goodyera repens is also a semi-mycoheterotrophic plant, which means it has an interesting symbiotic relationship with a fungus called Ceratobasidium cornigerum.
Dwarf rattlesnake plantain can make its own food, although it also utilizes this fungus to provide for some of its carbon intakes while exchanging nutrients with it.
How to Propagate Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain (Goodyera repens)


Hardiness Zone: 2-5
Soil Type: Loam, sand, or peat.
Water: Normal.

Exposure: Shade to Partial Shade.
According to my observations, there are a couple of ways to propagate dwarf rattlesnake plantain (Goodyera repens).
Let’s take a look:
How to Propagate Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain by Division
Being a rhizomatous plant, it’s possible to propagate it by division.
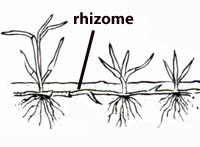
One mother plant could have sent off shoots underground where baby clones have come up from.
Division is an effective way to propagate dwarf rattlesnake plantain, here’s how you can do it:
By the way, the best time to divide is during spring, early summer, or fall.
Here’s how to do it:
- Find a wild patch of dwarf rattlesnake plantain and identify the largest plants.
- Dig a little and look closely to see the rhizomes going away from the mother plant.
- It should lead you to a clone further down, now all you need to do is dig it out.
- Snip a part of the horizontal rhizome with it and separate the clone from its mother, make sure to keep it moist until you transplant.
- When you transplant, you want to remove any dead or diseased foliage.
- Pot them individually and water them thoroughly.
- Keep away from direct sunlight until it establishes itself well.
Warning: Since dwarf rattlesnake plantain is a rare plant. Divide like this only what you need, and please leave many plants behind.
Note: Be cautious to divide plantain only before or after blooming, not during. Blooming takes a lot of energy from the plant, it’s not a good time to stress it at that point.
How to Propagate Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain (Goodyera repens) by Seed
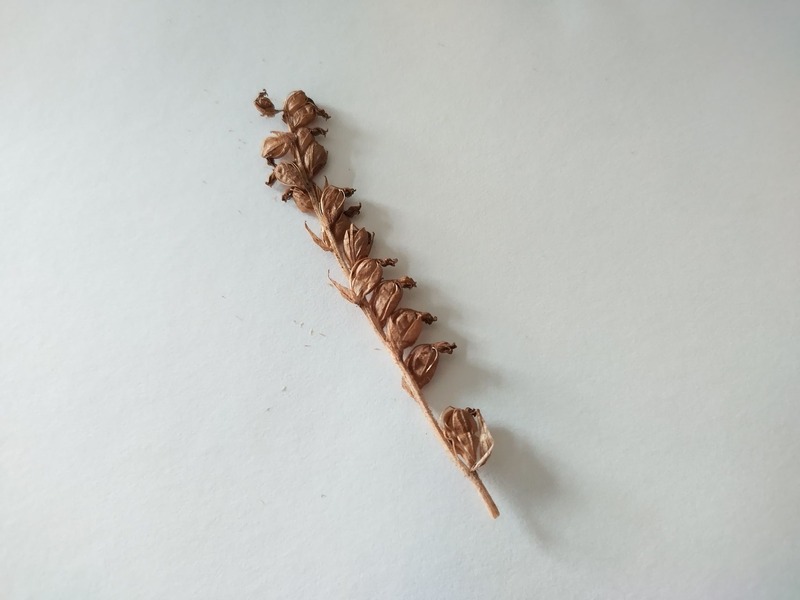
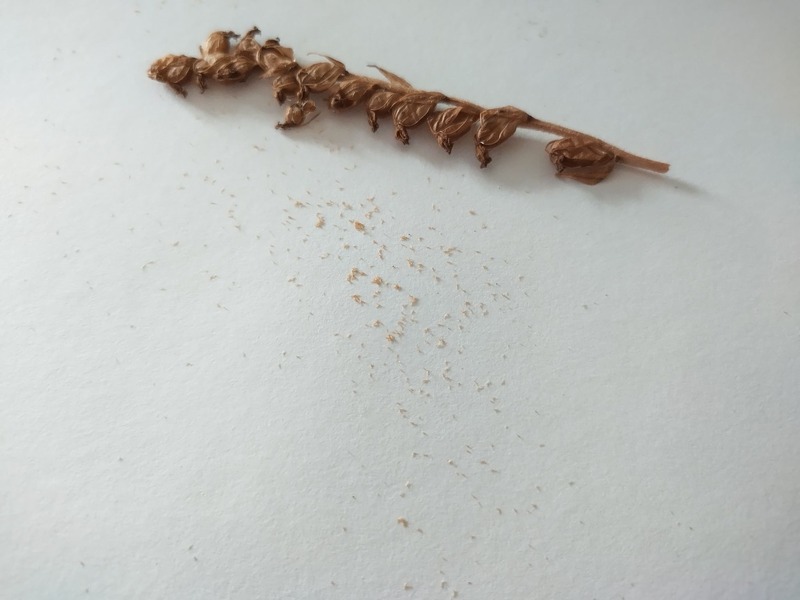
I’ve collected what I think to be dwarf rattlesnake seeds from their seed pods in autumn. Although they are very minuscule, I do think the tiny specs seen here below are the seeds.
There is not much literature online about their seeds, the only credible source I’ve found is from the USDA.
As far as I know, these are the first published images of goodyera repens seeds.


Now to propagate dwarf rattlesnake plantain by seed seems fairly difficult. According to USDA, lesser rattlesnake plantain requires a mycorrhizal symbiont (Rhizoctonia goodyerae-repentis) for seed germination and early seedling development.
But, according to their lab results, they can still be germinated without a symbiont as long as there is an external carbohydrate source. Additionally, inoculated seeds can also germinate without the presence of carbohydrates.
Also note that rhizomes arising from seed require 5 years to produce a rosette of evergreen leaves, which produces a flowering stalk and seed capsules after approximately 3 more years.
Will return in 8 years… to share my results!
Read the USDA’s notes on dwarf rattlesnake regeneration here.
FAQ
Q: What’s another name for Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain?
A: Other names for Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain include Creeping Lady’s Tresses & Lesser Rattlesnake Plantain.
Q: Is Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain an Orchid?
A: Yes, it is part of the orchidae family of flowers. Which means it has the feminine and masculine organs of reproduction fused in only one body called a column or gynostemium. Orchid flowers have an irregular form made up of three sepals and three petals. The medium petal is modified and is called the labellum or lip.
Q: Where geographically can you find Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain?
A: According to Adirondack Wildflowers, it can be found on the Boreal Life Trail at the Paul Smiths VIC, or alternatively along Sucker Brook Trail at the Adirondack Interpretive Center. Personally, I have found my specimens at Lake Paradis, in the Matagami region of Quebec.
Q: Is Dwarf Rattlesnake Plantain Edible?
A: No, but it has been used as a medicinal plant by the Cherokee as a blood tonic, burn dressing, and cold remedy.


