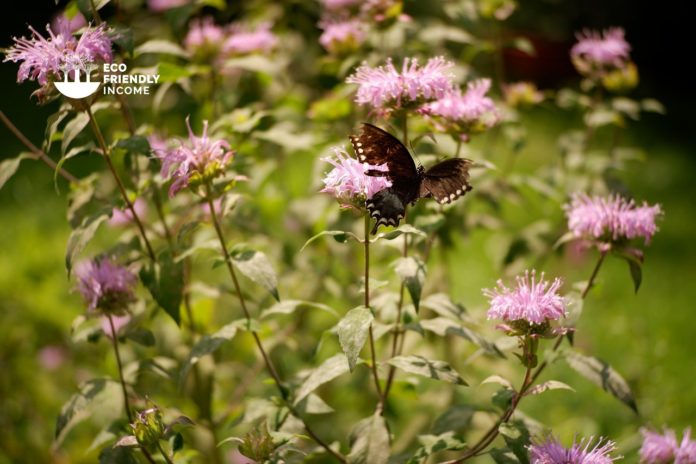
A field guide on how to identify and propagate Wild Bergamot (Monarda fistulosa), a zone 2 perennial shrub native to North America.

Hardiness Zone: 2-8
Soil Type: Well-drained Loam, Sand, or Clay.
Water: Normal.

Exposure: Full Sun to Partial Shade.
How to Identify Wild Bergamot (Monarda fistulosa)
Leaves
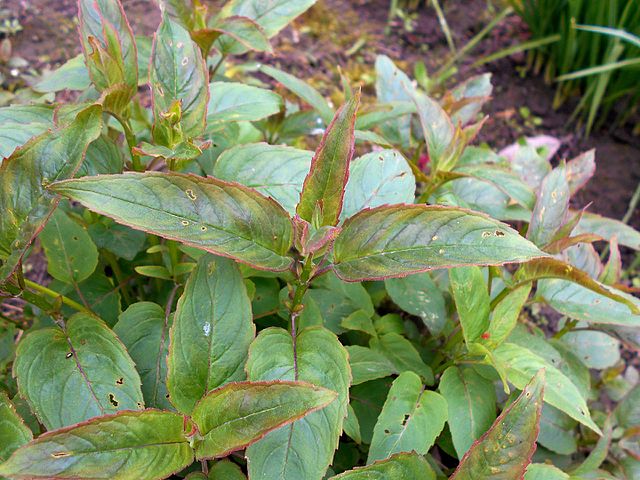

The leaves of wild bergamot grow in opposite arrangements, are lance-shaped, have serrated margins, and are about 2-4 inches long. They are green, have a hairy texture, and can have a red tinge on the edges.
The leaves are also very aromatic and have a smell similar to oregano.
Flowers

The wild bergamot flowers are purple and have a strong, sweet smell. They grow in clusters and are about 2-3 inches across.
The petals are long and tubular, and they curve inward at the tips.
Flowering Season
The flowering season of monarda fistulosa is typically from July and August. The blooms last about 6 weeks.
Habitat
Monarda fistulosa is a perennial herb that is native to eastern North America.
It typically grows in moist, open areas, such as meadows, prairies, and woodlands.
Today its range is massive, from the Southern States up to the Northern Boreal Forests in Canada.
Wildlife Value
Wild bergamot, or bee’s balm is a valuable nectar source for bees and other pollinators. The flowers are also attractive to butterflies and hummingbirds.
It is also a larval host plant for the black swallowtail butterfly.
How to Propagate Wild Bergamot (Monarda fistulosa)
There are many techniques that can be used to propagate wild bergamot. Some of these techniques include division, seed, and cuttings.
- Division involves taking a large mother plant and splitting its clones into many seperates plants.
- Seed involves harvesting the wildflower seeds, roughly 4 weeks after flowering.
- Cuttings involve taking pieces of fresh, vigorous growth from plants and setting them in an envionment to form new roots.
Let’s get into more details for each technique:
Division
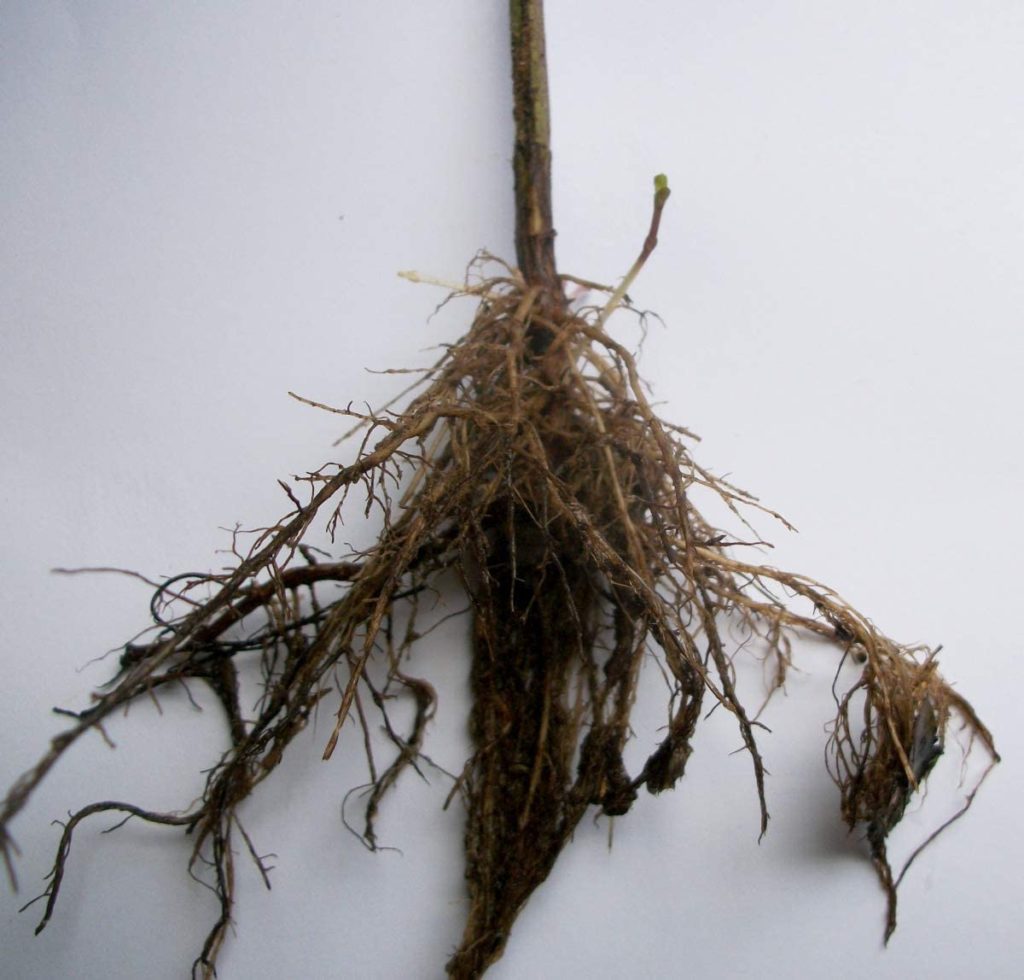

Division is probably the easiest way to propagate wild bergamot because the plant naturally spreads by rhizome.
This means it naturally sends out shoots, further down that are still attached to the mother plants. All you need to do is identify the clones, separate the rhizome and uproot them.
The best time to divide wild bergamot is during early Spring, as soon as new growth appears.
Here’s how:
- Select a healthy, vigorous bergamot plant.
- Dig around it, and uproot a clump of stems, shake off the dirt.
- Divide the plant into two or more sections, making sure each section has at least one healthy bud, and some roots.
- Replant the divisions in well-drained soil, making sure the buds are pointing up.
- Water the plants regularly and fertilize them once a month.
Seed

Germinating seeds is a sure way to propagate wild bergamot.
Their seeds are hidden inside these capsules that are left over after the flower blooms.
They are very tiny so timing here is important if you want to get the most out of each seedhead.
Collect them when they are near this stage, but not completely dry yet. Leave them to dry at home in a brown paper bag for some time.
Next, shake the bag carefully and you will get hundreds of tiny seeds.
How to germinate them is just like any other wildflower:
- Soak the seeds in water for 24 hours.
- Spread the seeds out on a damp paper towel and fold the towel over.
- Next, put the towel in a plastic bag and seal the bag.
- Store the bag in a warm place (70-75 degrees F).
- Check the towel every day to make sure it remains damp.
- Finally, the seeds should germinate in 10-14 days.
Wild bergamot seeds can germinate without a cold-stratification period.
Cuttings
You can also propagate wild bergamot by taking plant cuttings from vigorous growth.
The best type of cuttings for this are softwood cuttings, which can be taken from early spring to mid-summer.

- First, spot a healthy bergamot plant and inspect each stem for new growth.
- Next, use a sharp, clean knife and cut a stem below a node. (You can take a longer stem and split it into 6 inch pieces.) Make sure each bottom cut is below a node.
- Strip off the lower leaves and cut off the flower buds, this is important to retain moisture and focus growth on roots.
- Prepare a propagating tub for the cuttings. A good propagating medium is 3:1 perlite to potting soil. It’s also good to have a top to cover the tub, this will keep moisture level high.
- Premake some holes with a dibbler.
- Next, dip the ends of each stem in rooting hormone, knock off the extra, then insert the stems into the mix and press down firmly.
- Water thoroughly, cover the tub and place in a well lit area, but not where it will get direct sunlight.
If the tub is fairly well sealed, humidity levels will stay high, and fog up the glass. That’s exactly what you want, cuttings need a high level of moisture to root.
Warmth also helps, if you have some heating mats, it can’t hurt to use one under your tubs to heat it up.
Periodically check on your tub, but you shouldn’t have to water often if it’s well sealed.
Wild bergamot cuttings take about 3-4 weeks to root.
After they’ve rooted, don’t rush to transplant, tilt the cover on the tub for a few days to let them acclimate to dryer air.
After they are acclimated, you can individually pot them or plant them outside.
That’s it! That should have you covered to propagate wild bergamot.
Want to propagate like a pro? Check out our ultimate plants propagation guide.
Looking for more zone 2 plants? Take a look at our list of zone 2 perennials.

