Today we take a look at an interesting part of the natural world, the fungi kingdom.
The question we look into today exactly is: What is the main function of species in the fungi kingdom?
To answer this question, we’ll get into the details and mechanics that help this kingdom thrive.
The Main Function of Fungi
The main function of fungi is to decompose organic matter.
Fungi secrete enzymes that break down complex molecules in dead plants and animals into simpler compounds that can be absorbed by the fungi. This process of decomposition is important for the recycling of nutrients in ecosystems.
Step by Step How Fungi Decomposition Works
- First, fungi secrete enzymes that break down complex organic molecules into smaller, more manageable pieces.
- Then the enzymes break down the bonds between molecules, making the molecules even smaller. At this point, the smaller molecules are now easier for fungi to absorb and use for energy.
- Finally, the fungi absorb the smaller molecules, getting the nutrients they need to grow and reproduce. The leftover organic matter is in a more simplified form that is easier for other organisms to decompose or absorb.
Fungi Structure
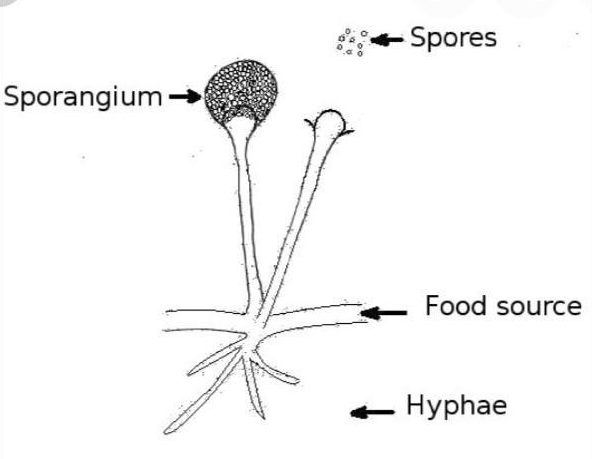
A simple breakdown of fungi into 4 parts:
- Sporangium: The structure that produces spores (the fruiting body we usually see on the surface).
- Spores: The small seed-like structures that fungi use to reproduce (usually spread by wind or water).
- Food source: The organic matter the fungi spores attaches themselves to (dead or living organisms).
- Hyphae: They are the long, slender, threadlike structures that make up the body of a fungus (like a root system).
If you look at this drawing, you can understand why fungi are decomposers. The “food source” is part of their organism, it’s necessary for them to break down organic matter to live.
The hyphae also play an important part in the fungi’s functions. This root-like system helps mineralize organic matter and can transfer these nutrients to plants.
Fungi Functions by Category
These 4 categories of mushrooms separate them by their behavior, do they all decompose organic matter?
Let’s find out:
- Saprotrophic: They are the first to decompose organic matter, growing on dead logs, and leafy matter breaking them down for nutrients.
- Mycorrhizal: They form symbiotic relationships with the roots of the plant. Mycorrhizal fungi help plants absorb water and nutrients from the soil, and in return, the plants provide the fungi with a source of food. They also replace saprotrophic mushrooms when organic matter is too decomposed for them to break down further.
- Parasitic: They are fungi that live on other living organisms (such as trees) and derive their nutrients from them. This means they are also decomposers, but prey on living organisms rather than dead ones.
- Endophytic: Endophytic mushrooms are mushrooms that grow inside plants and form a symbiosis with them. They help plants decompose metabolites.
4 Other Functions of Fungi
Decomposition is not the only function of the fungi kingdom. They are carbon cyclers; soil formers; nutrient mineralizers and utilizers; protectors from pathogens and herbivores; and controllers of plant and insect populations.
1. Carbon Cycling
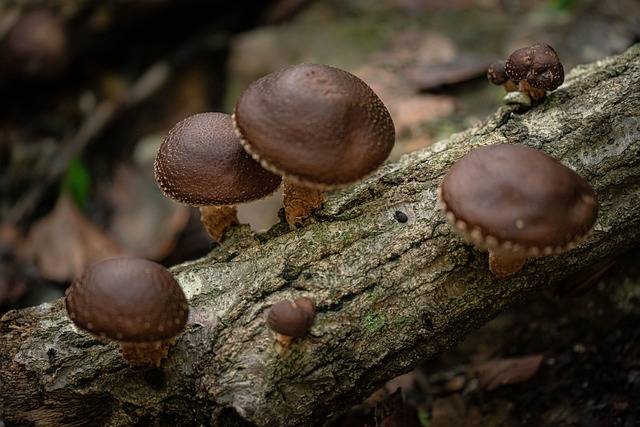

Fungi that decompose wood play an important role in the global carbon cycle. By breaking down wood, they make the carbon stored in it available to build soils, and microbial communities, and ultimately nourish plants.
2. Soil Formation, Nutrient Mineralization & Utilization

Formation: Fungi such as oyster mushrooms and chicken of the woods break down cellulose that helps create new soil.
Mineralization: As these fungi dine, some of the nutrients leak into their surrounding environment. These nutrients that escape digestion become “mineralized” in the soil and help form the base of the terrestrial food web.
Utilization: Mycorrhizal fungi such as chanterelles aid the growth of their symbionts by scavenging and transferring important minerals nutrients.
3. Protection from Pathogens & Herbivores
As mentioned above, mycorrhizal fungi transfer important minerals nutrients to plants. One of the important minerals they transfer is phosphate, which helps plants resist disease and pests.
Fungal endophytes that colonize plants also provide them with protection against herbivory insects. These endophytes cause insects to have a lower growth rate, developmental rate, and survival rate.
4. Controlling Plant & Insect Populations
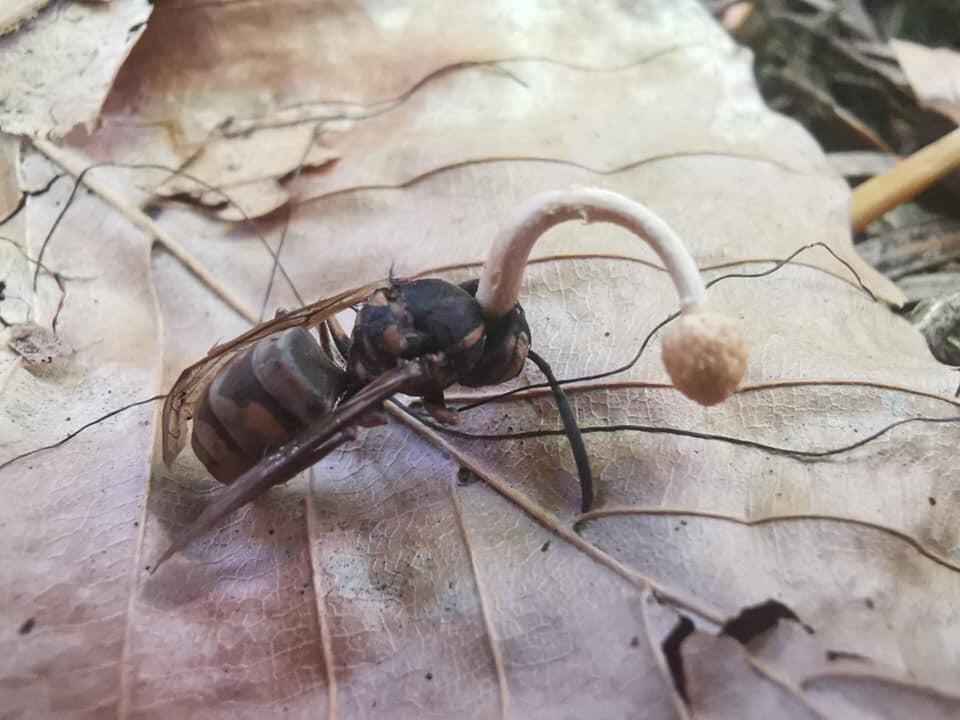

Entomopathogenic fungi are a group of fungi that kill insects by infecting them and feeding on their bodies. These fungi live in the soil and penetrate the insects’ cuticles to enter their bodies.
Fungi can also cause foliage disease in plants that can eventually kill them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we see that the main function of the fungi kingdom is to decompose organic matter, but it’s not all.
Fungi are also important for carbon cycling, soil formation & mineralization. They also help plants utilize nutrients in the soil, and help protect them against insects and diseases.
They also help keep insect and plant populations in check by infecting and killing them.
FAQ
Q: Do mycorrhizal fungi decompose organic matter?
A: Yes, as the organic matter decomposes, mycorrhizal fungi replace saprotrophs as the main decomposers.
Q: Do endophytic fungi decompose organic matter?
A: Yes, microscopic endophytic mushrooms attached to the roots of plants or found in soil do synthesize and decompose metabolites.

